How to Find My Router IP Address on Any Device

Ever wondered how to access settings on your router or secure your home network? It's all about finding that little string of numbers, otherwise known as the IP address. This small string of numbers acts as the gateway into your network, enabling you to manage settings for Wi-Fi, connectivity troubleshooting, and even advanced tool setups such as a VPN.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to find your router's IP address on any device, be it Windows, Mac, Android, iOS, or Linux. We'll be sure to include clear steps, practical tips, and essential nuances for the complete beginner looking to familiarize themselves with complex terms in simple language. By the end, you will know not only your router's IP but also why it matters in order to keep your network secure and optimized, especially when working with a VPN service like GuruVPN.
What is a Router IP Address?
Before specific device instructions are provided, it's first necessary to understand what a router IP address actually is. In simple terms, your router's IP address is what allows your devices to communicate with the router, and in turn with the internet.
There are two types of IP addresses to know:
- Public IP Address. This is the IP address that is assigned to your network by your ISP. It is what websites and online services see when you are browsing the internet.
- Private IP Address. This is the IP used inside your home or office network. Each device-laptop, smartphone, smart TV-communicates with your router through this private IP.
Most routers use standard private IP addresses, such as 192.168.0.1, 192.168.1.1, or 10.0.0.1. The reason why you need to know this IP is because you can access an admin panel of your router, change settings, troubleshoot, and even create a VPN to secure the network traffic.
Why does it matter for security? The knowledge of a router's IP opens a wide range of possibilities to secure one's Wi-Fi, change default passwords, or enable VPN support. Without it, you won't be able to make the necessary changes to keep your network safe.
How to Find Your Router’s IP Address on Windows
Finding your router’s IP address on Windows is straightforward, and you can do it in two different ways: through the Command Prompt or through the graphical interface. Below are both methods, so choose whichever feels more comfortable.
Method 1: Using Command Prompt (Fastest Way)
- Press Win + R on your keyboard.
- Type cmd and press Enter, this will open the Command Prompt.
- In the Command Prompt window, type:
ipconfig and press Enter.
- Scroll through the results until you find the section for your active network adapter (Wi-Fi or Ethernet).
- Look for the line called Default Gateway, this number is your router’s IP address.
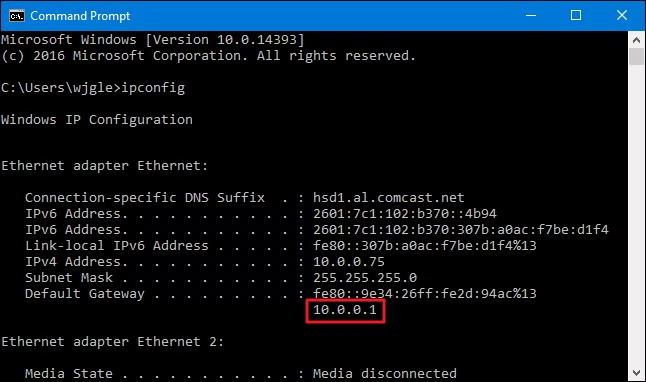
What it’ll look like on your computer. Source: Howtogeek
Tip. If you see multiple adapters (like “VirtualBox” or “Bluetooth”), ignore them and look for the one that shows IPv4 and DNS values.
Method 2: Using Windows Network Settings (No Commands Needed)
- Open Settings from the Start menu.
- Go to Network & Internet.
- Select Wi-Fi (if you're connected wirelessly) or Ethernet (if you’re using a cable).
- Click on your active network.
- Scroll down to the Properties section.
- Look for Default Gateway - this is your router’s IP address.
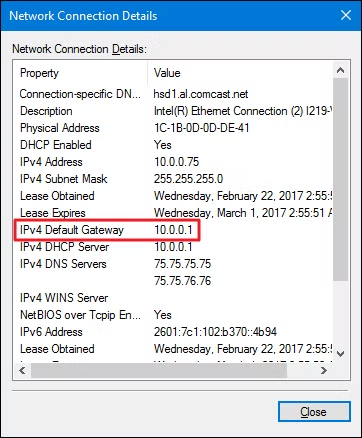
You should find this. Source: Howtogeek
Note. The layout may vary slightly depending on your Windows version (Windows 10 vs. Windows 11), but the information is always in the network’s Properties screen.
Common Nuances on Windows
- If you’re connected to a guest network or a shared hotspot, the Default Gateway may not appear.
- If you see an address like 169.254.x.x, this means your system isn’t connected properly - try reconnecting to Wi-Fi.
- For advanced users, you can also find the gateway using PowerShell with:
Get-NetIPConfiguration | Select-Object -ExpandProperty IPv4DefaultGateway
How to Find Your Router’s IP Address on Mac (macOS)
macOS makes it easy to locate your router’s IP address through the system settings, but you can also use the Terminal if you prefer a command-line method. Both approaches are simple and reliable.
Method 1: Using System Settings (Most User-Friendly)
- Click the Apple menu in the top-left corner.
- Open System Settings (or System Preferences on older macOS versions).
- Select Network from the sidebar.
- Choose your active connection: Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
- Click Details (macOS Ventura and newer) or Advanced… (older versions).
- Navigate to the TCP/IP tab.
Look for the field labeled Router - the number you see here is your router’s IP address.
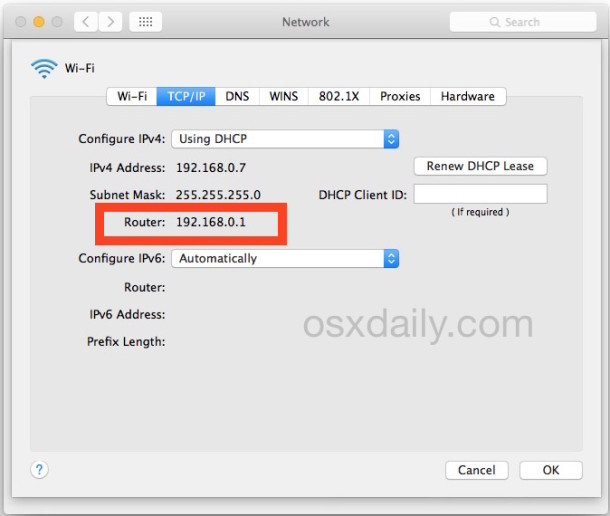
Source: OSXDaily
Tip. If you’re using macOS Monterey or earlier, the menu labels might differ slightly, but the information is always under the TCP/IP tab.
Method 2: Using the Terminal (For Quick Access)
- Open Terminal (Applications → Utilities → Terminal).
- Enter the command:
netstat -nr | grep default
- The number shown next to default is your router’s IP address.
Alternative command:
route -n get default | grep gateway
This provides the gateway address in a super-clean format.
Common Nuances on macOS
- If you're connected to a VPN, macOS may show the VPN interface first - make sure you're checking the Wi-Fi or Ethernet adapter.
- If “Router” appears blank in the TCP/IP settings, your Mac may not be properly connected to the network - try toggling Wi-Fi off and on.
- For mesh systems (e.g., Eero, Google Nest WiFi), the router IP may differ from usual defaults (e.g., 192.168.86.1).
How to Find Your Router’s IP Address on Android
Android devices provide quick access to network details, including your router’s IP address. However, menu names and layouts can vary slightly depending on your phone manufacturer (Samsung, Xiaomi, Google Pixel, etc.) and your Android version.
Method 1: Through Wi-Fi Settings (Most Common)
- Open the Settings app on your Android device.
- Go to Wi-Fi or Network & Internet.
- Tap on your connected Wi-Fi network (usually shows the network name/SSID).
- Look for Advanced, Additional settings, or Network details - the wording depends on your phone.
- Find the field labeled Gateway - this number is your router’s IP address.
Tip. On many devices (Google Pixel, OnePlus, Motorola), the router’s IP appears immediately under “Gateway.” Samsung devices may list it under View more or IP settings.
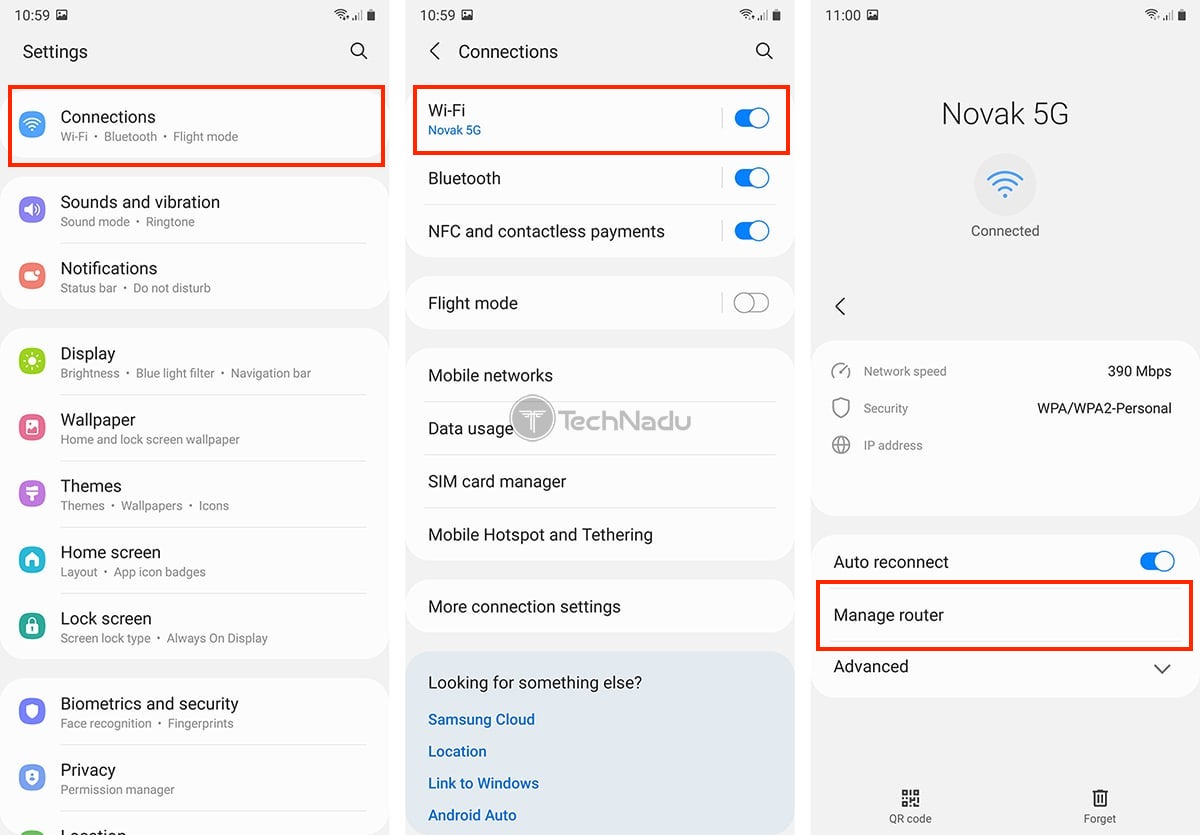
Source: TechNadu
Method 2: Using a Network Info App (Optional)
If your phone’s interface hides advanced network details, you can use a third-party app (e.g., “WiFi Analyzer,” “IP Tools,” or “Fing”). These apps typically display the router’s IP as Gateway or Default Gateway.
Note. You don’t need these apps for security purposes - they’re just helpful if your phone buries the network information deeply in menus.
Common Nuances on Android
- Your router’s IP will only appear when you're connected to Wi-Fi - mobile data networks (4G/5G) do not expose router information.
- Some Android skins (MIUI, EMUI) may require tapping More settings before showing the Gateway field.
- If you see an IPv6 address instead of IPv4, scroll further - the router’s IPv4 address (e.g., 192.168.x.x) is usually listed separately.
- If the Gateway field is blank, toggle Wi-Fi off and back on to refresh the network info.
How to Find Your Router’s IP Address on iOS (iPhone/iPad)
Apple makes it very easy to find your router’s IP address on iPhone and iPad. The information is located right inside the Wi-Fi settings, and you can access it in just a few taps.
Method: Through Wi-Fi Settings (Quickest and Easiest)
- Open the Settings app on your iPhone or iPad.
- Tap Wi-Fi.
- Make sure you’re connected to a network, then tap the (i) icon next to your Wi-Fi name.
- Scroll down to the IPv4 Address section.
- Look for the field labeled Router - this number is your router’s IP address.
That’s it - no extra tools or apps required.
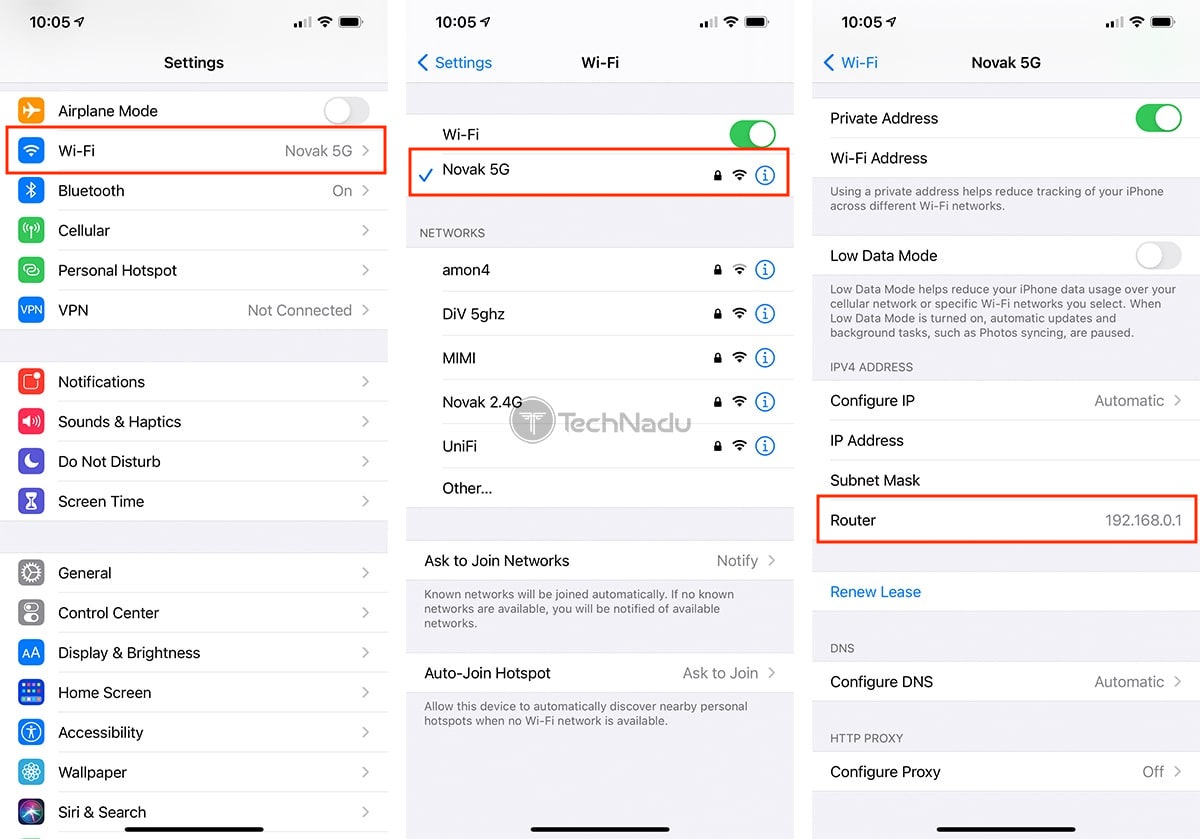
Source: TechNadu
Nuances on iOS
- The router IP will only appear when you’re actually connected to Wi-Fi.
- On networks that use advanced configurations (e.g., enterprise Wi-Fi or mesh systems), you may see multiple IP fields - the one labeled Router is always the correct one.
- If the field is empty or greyed out, try reconnecting to Wi-Fi or resetting the network settings (Settings → General → Transfer or Reset iPhone → Reset → Reset Network Settings).
- For VPN users: if a VPN is active, iOS may prioritize virtual network interfaces - but the Router field under Wi-Fi always shows the true gateway IP for your local network.
How to Find Your Router’s IP Address on Linux
Linux provides several easy ways to discover your router’s IP address. Whether you prefer using the terminal or a graphical interface, the process is simple and works across most distributions, including Ubuntu, Fedora, Linux Mint, Debian, and others.
Method 1: Using the Terminal (Most Reliable Method)
You can find the router’s IP with a single command:
- Open the Terminal.
Enter the following command: ip route | grep default
- Look for the value after default via - this is your router’s IP address.
Example output:
default via 192.168.1.1 dev wlan0
Here, 192.168.1.1 is the router’s IP.
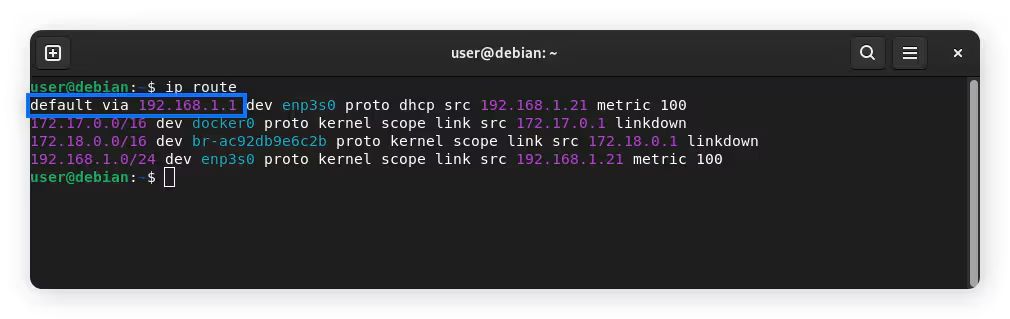
Source: Norton
Alternative Terminal Command
If the above doesn’t work on your system, try:
route -n | grep 'UG[ \t]'
You’ll see a row beginning with your router’s IP under the Gateway column.
Method 2: Through Network Manager (GUI Method)
If you're using a desktop environment like GNOME, KDE, Cinnamon, or XFCE:
- Click on the network icon in the system tray.
- Choose Network Settings or Wi-Fi Settings.
- Select your active Wi-Fi or Ethernet connection.
- Navigate to the IPv4 (or sometimes Details) tab.
- Look for the field labeled Default Route, Gateway, or Router - this is your router’s IP address.
Note! Menu names vary slightly between distros, but “Gateway” is always the value you're looking for.
Common Nuances on Linux
- Some distros display IPv6 routing first; make sure you’re viewing IPv4 if you need the classic local network IP (like 192.168.x.x).
- If you're connected through a VPN, some commands may list multiple gateways - the correct gateway for your router is tied to your Wi-Fi or Ethernet interface (e.g., wlan0, eth0).
- If
ip routedoesn’t show a gateway, your connection may be misconfigured - try reconnecting to the network or checking Network Manager.
For advanced users: nmcli dev show | grep IP4.GATEWAY
This command works on any system with NetworkManager.
Practical Tips and Troubleshooting
Even though finding your router’s IP address is usually straightforward, certain scenarios or network configurations can make the process less obvious. Below are practical tips and troubleshooting steps to help you quickly resolve any issues and understand what’s happening inside your network.
1. If You Can’t See the Router IP at All
If you don’t see a Default Gateway or Router address on your device:
- Reconnect to your Wi-Fi network. Sometimes the device just didn’t obtain proper network information.
- Restart your router. A simple reboot often fixes incorrect or missing gateway assignments.
- Disable and re-enable Wi-Fi. This forces the device to refresh its IP configuration.
- Check if you’re on mobile data. You must be connected to Wi-Fi to see a router IP.
2. If You See “169.254.x.x” as Your IP
This type of address is called APIPA, and it means your device failed to get a valid IP from the router.
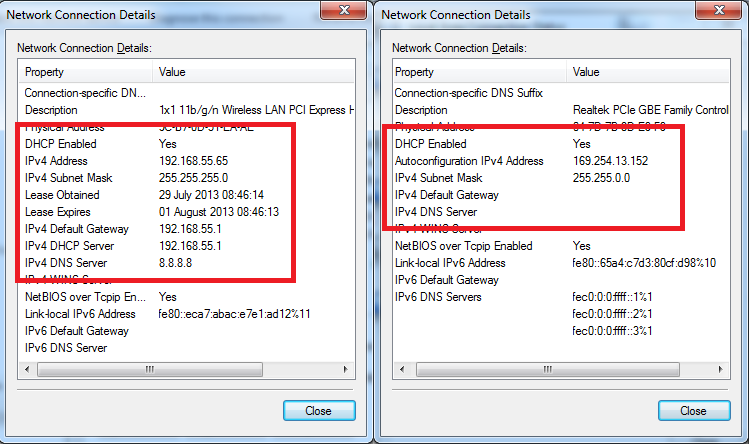
Source: Blue Compute
To fix this:
- Restart Wi-Fi.
- Forget the network and reconnect. Restart the router.
- Check if DHCP is enabled in your router settings.
3. If You’re Connected Through a VPN
VPNs can add virtual network interfaces, which sometimes complicate things:
- Always view the router IP under your physical interface:
- Wi-Fi
- Ethernet
- The VPN interface will not show your actual home router’s gateway.
Tip! If the gateway appears wrong, temporarily disconnect the VPN, find the router IP, then reconnect.
4. If You’re Using a Mesh Wi-Fi System
Mesh systems (Eero, Google Nest, TP-Link Deco, Orbi) sometimes use non-standard private IP ranges. That’s normal.
Common mesh router IP examples:
- 192.168.86.1 (Google Nest WiFi)
- 172.16.0.1 (some enterprise-style systems)
Don’t panic if it doesn’t look like the usual 192.168.x.x - the process is still the same.
5. Ensure You’re Checking the Correct Network Adapter
On devices with multiple adapters (Windows PC with VPN, virtual machines, Ethernet, Wi-Fi):
- Look specifically for the active network adapter.
- Ignore adapters like:
- Bluetooth
- VirtualBox or VMware hosts
- Disabled Ethernet ports
These can show irrelevant gateway values.
6. Ping the Router to Verify It’s Reachable
Once you’ve found the router IP, you can verify it’s working:
Windows/macOS/Linux Terminal:
ping 192.168.1.1
If you receive responses, your router is functioning correctly.
If not:
- You might be connected to the wrong network.
- The router may be misconfigured or frozen.
- Try restarting the router.
7. Resetting the Router (Only If Needed)
If you cannot access your router at all:
- Press and hold the Reset button on the back of the device for ~10 seconds.
- This restores factory settings - including the default router IP.
Important! Only do this if you’re comfortable reconfiguring your Wi-Fi network afterward.
8. Security Reminder
Once you access your router:
- Always change the default admin password.
- Keep firmware up to date.
- Consider using a VPN directly on your router for improved security.
GuruVPN supports router-level configurations, making it easier to protect every device on your network.
Why Knowing Your Router’s IP Address Matters for VPN Users
If you’re using (or considering using) a VPN, knowing your router’s IP address becomes even more important. Your router is the central point of your home network, and many advanced VPN features depend on accessing your router’s settings.
1. Setting Up a VPN Directly on Your Router
Installing a VPN at the router level allows every device connected to your Wi-Fi - phones, laptops, smart TVs, game consoles - to benefit from secure, encrypted traffic without installing apps individually.
To configure GuruVPN on a router, you will need to:
- Access your router’s admin panel.
- Locate the VPN or WAN settings.
- Enter your GuruVPN configuration details.
And to do that, the very first step is knowing your router’s private IP address.
2. Enhancing Network-Wide Security
Your router IP gives you access to security settings such as:
- Enabling WPA3 or strong encryption protocols
- Changing default login credentials
- Blocking unknown devices
- Updating firmware
These steps are essential to keep your network safe - and a VPN like GuruVPN adds an extra layer by encrypting all outgoing traffic.
3. Solving VPN Connectivity Issues
When your VPN isn’t working properly, a misconfigured router is often the root cause. Being able to log in to your router helps you troubleshoot issues like:
- Incorrect DNS settings
- Firewall rules blocking VPN connections
- Conflicts with guest networks
- Outdated firmware causing stability problems
Knowing how to access your router allows you to quickly diagnose and fix these problems.
4. Understanding How Devices Route Traffic
A VPN creates a secure tunnel for your internet traffic. But the router is the device that decides how traffic moves between your local network and the outside world.
By accessing your router (via its IP address), you can:
- Confirm if the VPN tunnel is active
- Check routing tables
- Adjust split tunneling settings (if supported)
- Optimize DNS routing for speed and privacy
This is especially useful for users who want maximum performance and stability with GuruVPN.
5. Better Control of Your Online Privacy
Your router contains logs, connected-device lists, and DNS configurations. Managing these properly strengthens your privacy, even before the VPN connection is established.
GuruVPN complements this by ensuring:
- Your ISP cannot see your browsing activity
- Your public IP address remains hidden
- All traffic leaving your network is encrypted
But again? you can only fine-tune your privacy setup if you know where to find (and how to access) your router.
Final Thoughts: Take Control of Your Network
Finding your router’s IP address may seem like a small technical task, but it opens the door to full control over your home network. Whether you’re adjusting Wi-Fi settings, improving security, setting up parental controls, or configuring a VPN, understanding how to access your router is the foundation for a safer and more reliable online experience.
With the right knowledge, you can:
- Keep your network secure
- Troubleshoot issues faster
- Optimize performance
- Set up router-level VPN protection
- Protect every device connected to your Wi-Fi
And this is where GuruVPN becomes a powerful ally. By integrating VPN protection directly into your router or using the GuruVPN app on your devices, you ensure that every connection leaving your network is encrypted, private, and shielded from intruders or prying eyes.
Take the next step in securing your digital life - try GuruVPN and protect your network with confidence.