Can Encrypted VPN Traffic Be Identified? A Clear Explanation

Many think a VPN makes them completely invisible online due to its encryption. They believe once it's on, their activities are hidden. The reality is a bit more complex.
VPN encryption is useful for keeping your online activity safe by protecting things like websites visited and data sent. But, encryption doesn't hide internet usage. There are still connections and data moving, some of which can be observed.
This is how people can tell when you're using a VPN. Networks don't need to read your data to see traffic patterns; they often just need to know how your internet traffic behaves. The information can help you have a better understanding about VPN.
What VPN Encryption Actually Protects
To understand traffic identification, it helps to clearly separate content from metadata.
A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, protecting:
- Your data
- The websites you visit
- DNS requests
- Login info, messages, and files
This encryption keeps your info private from anyone monitoring your connection, like ISPs or public Wi-Fi providers.
That being said, some data is still visible:
- The fact that you're using a connection
- The IP address you're linking to
- Packet sizes and how quickly data is transferred
- Total data usage
Even though your data is encrypted, network observers can still infer some things about your online activity by analyzing these visible data points. This is a vital concept in understanding encrypted traffic inspection.
What Is VPN Traffic Identification?
VPN traffic ID is all about spotting when a connection is using a VPN, but without snooping on what's being sent.
Instead of checking the content, networks look at things like where the traffic is going, how the data packets are set up, and how steady the data flow is over time. The idea is to tag the VPN tunnel itself, not to see what's inside.
You'll usually see this kind of ID used by:
- Internet companies
- Company and school networks
- Content sites that have rules about regions or policies
- *Networks that need to filter stuff because of rules
Now, just because a network IDs VPN traffic doesn't mean they're blocking or watching it. A lot of times, they just sort it into a different category than regular web traffic.
VPN vs VPN Traffic Identification: What’s the Difference?
People often confuse VPN identification and VPN traffic identification, even though they're different. Knowing the difference helps you see how encrypted connections can still be spotted, even if they can't be decrypted.
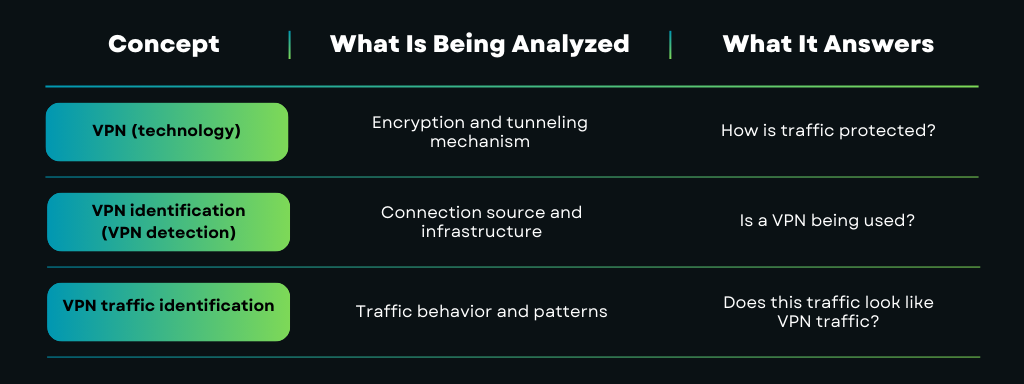
In simple terms, a VPN protects content, while identification techniques focus on context and behavior.
Encrypted traffic inspection might sound scary, but it's not as intrusive as you think. It doesn't mean peeking at your VPN data. It's more about looking at the features of encrypted connections.
Instead of reading the content, inspection checks the traffic's pattern. Networks might check things like packet timing, size, how long the connection lasts, and how the data flows. This tells them what kind of traffic it is without seeing what's inside.
You'll often find this type of inspection in company networks or places with strong traffic rules. It's there to sort and control traffic, not to spy on what you're doing.
Common VPN Traffic Identification Techniques
Normal VPN detection usually just checks IP addresses. But traffic identification looks at how encrypted data acts over time. Mixing these methods often makes things more accurate.
Traffic Flow and Packet Behavior Analysis
One of the most common techniques involves analyzing the structure and rhythm of encrypted traffic.
VPN connections often generate:
- long-lived, continuous encrypted sessions;
- relatively stable packet sizes;
- consistent upstream and downstream flow patterns.
This behavior differs from typical web browsing, which tends to be burst-based and more irregular.
What this reveals? Whether traffic resembles a persistent encrypted tunnel rather than standard HTTPS sessions.
Timing and Packet Interval Analysis
Even when packet contents are encrypted, the timing between packets remains observable.
Systems analyze:
- packet frequency;
- burst intervals;
- idle-to-active transition patterns.
VPN protocols often maintain regular keep-alive traffic or predictable timing behavior.
What this reveals? Statistical signatures associated with VPN protocols rather than casual browsing.
Protocol Handshake Fingerprinting
Every VPN protocol uses a handshake process to establish encryption keys and session parameters. While the handshake is encrypted, its sequence and structure can still be fingerprinted.
Advanced systems look for:
- protocol negotiation order;
- characteristic message lengths;
- transport-layer behavior during connection setup.
What this reveals? The likely protocol family (for example, modern VPN vs generic TLS traffic).
Transport Layer Characteristics
VPNs operate over transport protocols such as UDP or TCP, often in ways that differ from standard web traffic.
Identification systems may analyze:
- preference for UDP over TCP;
- retry and retransmission behavior;
- congestion handling patterns.
What this reveals? Traffic optimized for tunneling rather than page-based content delivery.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) Without Decryption
Despite the name, DPI does not decrypt VPN traffic. Instead, it examines:
- packet headers;
- flow consistency;
- encapsulation behavior.
DPI engines correlate these traits with known encrypted traffic models.
What this reveals? Whether traffic matches known VPN encapsulation profiles.
Correlation Across Sessions
More advanced systems track traffic behavior across multiple sessions or connections.
They look for:
- repeated connection behavior;
- consistent traffic signatures across IP changes;
- similar usage patterns over time.
What this reveals? Long-term behavioral indicators of VPN usage rather than single-session detection.
Why Traffic Identification Is Probabilistic
It’s important to note that VPN traffic identification is rarely definitive. Each technique provides partial confidence, not absolute proof.
Modern detection systems work by:
- combining multiple weak signals;
- assigning likelihood scores;
- adjusting thresholds based on policy or risk tolerance.
This is why false positives occur - and why VPN detection is best understood as classification, not confirmation.
Can Encrypted VPN Traffic Be Decrypted?
Normally, if your VPN encryption is set up right, people watching your network can't read it.
VPNs today use really strong ways to scramble your data and keep the keys safe. So, if someone grabs your internet traffic, it'll just look like gibberish without those keys.
Usually, the only time someone can read your VPN data is if something else goes wrong. Like if your phone or computer has a virus, or if you're using a really old or weak VPN setup. These problems usually affect your device, not the VPN itself.
It's important to know the difference. Identifying traffic skirts around the encryption instead of breaking it.
How Modern VPNs Reduce Traffic Identification
Modern VPNs approach traffic identification as a technical problem rather than a purely cryptographic one. Since encryption alone does not hide traffic patterns, mitigation focuses on reducing identifiable characteristics at the protocol and transport layers.
One of the key factors is protocol design. Contemporary VPN protocols avoid fixed packet structures and predictable handshake sequences that can be easily fingerprinted. Instead, they rely on minimal, consistent message formats that blend more naturally with other encrypted traffic.
Another important aspect is port and transport flexibility. Modern VPN implementations are not bound to specific ports and can operate over widely used transport protocols. This makes simple port-based filtering far less effective and reduces the visibility of VPN-specific signatures.
Traffic behavior also plays a role. Well-designed VPNs aim to maintain stable encryption and flow characteristics across sessions, avoiding patterns that sharply differ from standard encrypted web traffic. While packet timing and size cannot be fully hidden, reducing anomalies helps limit classification accuracy.
Some VPN solutions additionally implement traffic obfuscation techniques, which modify packet presentation without weakening encryption. These techniques do not change the protected content but make VPN traffic harder to distinguish from other encrypted connections at a superficial level.
Finally, implementation quality matters as much as theory. Even strong protocols can become easy to identify if deployed with static configurations, legacy fallbacks, or inconsistent encryption settings. Modern VPNs prioritize uniform behavior across devices and networks to minimize unintended exposure.
Together, these measures do not promise invisibility, but they significantly raise the technical threshold required to reliably identify VPN traffic - which is the realistic goal in modern network environments.
Why This Matters for Everyday VPN Users
For most users, VPN traffic identification is more about access and reliability rather than secrecy.
If a network sees VPN traffic, it might slow it down, block it, or handle it in a special way. This can mess with your connection on public Wi-Fi. And on some networks, it might decide if you can use a VPN or not.
Knowing how networks spot VPNs helps you pick the right VPN, choose the right settings, and know what to expect.
Common Myths About VPN Traffic Identification
One common myth is that a VPN makes you completely invisible online. In reality, it makes your activity private, not nonexistent.
Another misconception is that encrypted traffic cannot be analyzed at all. While its contents are protected, its behavior is not entirely hidden.
Finally, not all VPNs handle identification equally. Protocol choice, implementation quality, and network behavior all play a role in how detectable a VPN connection is.
Privacy Comes From Understanding the Boundaries
VPNs are powerful privacy tools, but they are not magic cloaks. They protect what matters most - your data and online activity - while operating within the technical realities of modern networks.
Understanding how VPN traffic identification and encrypted traffic inspection work helps set realistic expectations and leads to better privacy decisions. At Guru VPN, our focus is on building connections that are secure, resilient, and designed for how the internet actually works today.