8 Simple Ways to Secure Your Home Wi-Fi Network

8 Simple Ways to Secure Your Home Wi-Fi Network
In one of our previous articles, we talked about how your IP address, router settings, and basic network security play a key role in protecting your online identity. We covered why your router is more than just a box that delivers internet - it’s the main gateway between your devices and the outside world.
Now, it’s time to take the next step and look closer at Wi-Fi security.
Why Securing Your Wi-Fi Matters?
Your Wi-Fi network connects everything you use daily - smartphones, laptops, smart TVs, home assistants, and even work devices. If it’s not properly secured, it can quietly become an open door for unauthorized users, data interception, or even direct attacks on your devices.
The good news? You don’t need to be a networking expert to lock it down.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through simple, practical steps to secure your Wi-Fi network, reduce common risks, and add an extra layer of protection to your everyday internet connection. These tips are easy to apply, work for most modern routers, and make a real difference in keeping your digital life private and secure.
Tip #1: Change Your Router’s Default Login Credentials
One of the most common Wi-Fi security mistakes is leaving your router’s default login credentials unchanged.
Most routers come with a standard username and password like admin / admin or admin / password. This information is widely known, easy to find online, and often the first thing attackers try when scanning for vulnerable networks.
If someone gains access to your router’s admin panel, they can:
- Change your Wi-Fi password without you noticing
- Monitor or redirect your internet traffic
- Open your network to unauthorized devices
- Disable security features altogether
What you should do
- Log in to your router’s settings (usually via a browser using an IP like 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1).
- Change the administrator username if possible.
- Create a strong, unique password that you don’t use anywhere else.
A secure router password should be long, unpredictable, and include a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols.
Why this matters
Your router is the control center of your entire Wi-Fi network. Securing access to it is one of the fastest and most effective ways to block unauthorized changes before they happen.
Once your router login is protected, you’ve already eliminated one of the easiest attack paths - and made your Wi-Fi network significantly harder to compromise.
Tip #2: Use Strong Wi-Fi Encryption (WPA3 or WPA2)
Wi-Fi encryption determines how well your data is protected while it travels between your devices and the router. Without proper encryption, anyone nearby could potentially intercept your traffic - even if your network has a password.
Many older routers still support outdated security standards that are no longer safe. Weak or obsolete encryption protocols make it easier for attackers to:
- Capture unencrypted data
- Crack your Wi-Fi password
- Monitor your online activity
- Gain access to connected devices
What type of encryption should you use?
- WPA3 - the most secure option available today. It offers stronger protection against password-guessing attacks and better privacy on modern devices.
- WPA2 (AES) - still safe and widely supported if WPA3 isn’t available.
You should avoid using:
- WEP - outdated and easily brokenWPA (TKIP) - no longer considered secure
- Open networks with no encryption at all
How to check and update your Wi-Fi encryption
- Open your router’s admin panel.
- Find the Wireless Security or Wi-Fi Settings section.
- Select WPA3 or WPA2 (AES) as the security mode.
- Save the changes and reconnect your devices if needed.
Why this matters
Strong encryption ensures that even if someone is within range of your Wi-Fi signal, they won’t be able to read or tamper with your data. It’s a core layer of protection that keeps your online activity private - especially when combined with other security measures.
With proper encryption in place, your Wi-Fi network becomes far more resistant to common attacks.
Tip #3: Create a Strong and Unique Wi-Fi Password
Your Wi-Fi password is the first line of defense protecting your network from unauthorized access. If it’s weak, predictable, or reused elsewhere, even strong encryption won’t fully protect you.
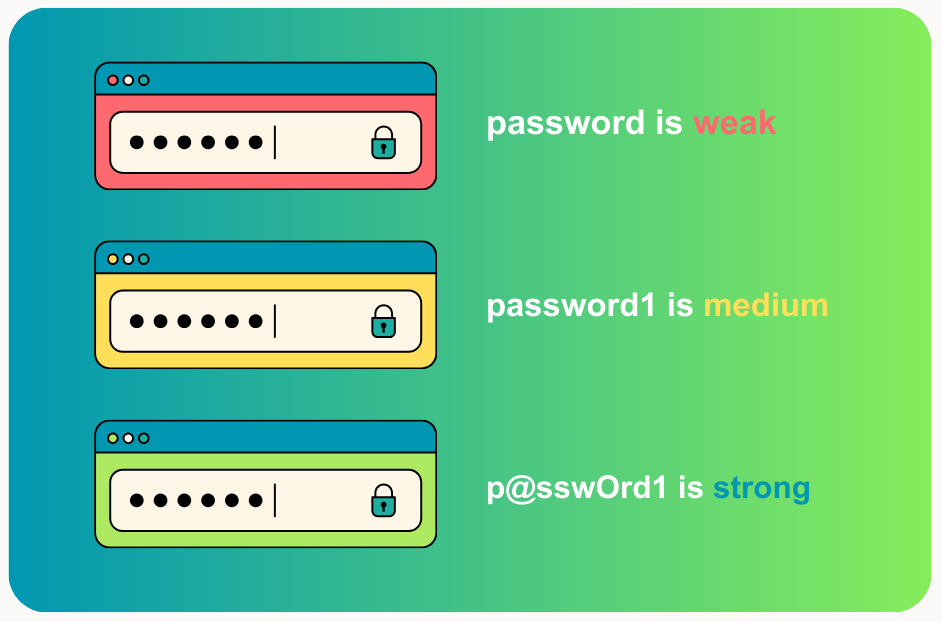
Many people still use simple passwords like their address, phone number, or variations of 12345678. These can be guessed or cracked surprisingly fast.
What makes a strong Wi-Fi password?
A secure Wi-Fi password should:
- Be long (at least 12–16 characters)
- Include uppercase and lowercase letters
- Use numbers and special symbols
- Avoid personal information or common words
The longer and more random the password, the harder it is to break.
Don’t reuse passwords
Your Wi-Fi password should be unique and not used for:
- Email accounts
- Social media
- Online services or subscriptions
Reusing passwords increases the risk that a single data breach could expose your entire network.
Sharing Wi-Fi safely
If you need to share your Wi-Fi:
- Use a guest network whenever possible
- Change your password periodically
- Avoid posting or sending your password in public or unsecured channels
Why this matters
A strong Wi-Fi password prevents unwanted devices from joining your network and reduces the risk of data interception or misuse. It also protects smart home devices that often lack advanced security features.
Combined with proper encryption, a strong password keeps your Wi-Fi private and under your control.
Tip #4: Keep Your Router Firmware Up to Date
Your router runs on firmware - built-in software that controls how it operates and how secure it is. Just like your phone or computer, a router needs regular updates to stay protected.
Many people never update their router after the initial setup, leaving known vulnerabilities unpatched for years. Router updates often:
- Fix security vulnerabilities attackers actively exploit
- Improve stability and performance
- Add support for newer security standards like WPA3
- Patch bugs that could expose your network
Outdated firmware can make even a well-configured Wi-Fi network vulnerable.
How to check for updates
- Log in to your router’s admin panel.
- Look for a section like Firmware, System, or Advanced Settings.
- Check for available updates and install them if needed.
Some modern routers support automatic updates, which is the safest option if available.
When should you update?
- Check for updates at least every few months
- Update immediately if your router manufacturer releases a security patch
- Restart your router after updating to apply changes properly
Why this matters
Keeping your router firmware up to date closes security gaps before they can be exploited. It ensures your Wi-Fi network stays resilient against evolving threats and continues to support modern protection features.
This simple habit dramatically reduces the risk of silent attacks on your home network.
Tip #5: Disable WPS and Unused Router Features
Modern routers often come with extra features designed to make setup easier. Unfortunately, some of these features can weaken your Wi-Fi security if left enabled. One of the most common examples is WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup).
Why WPS can be risky
WPS allows devices to connect to your Wi-Fi using a PIN or a push button instead of a password. While convenient, it has known security flaws that attackers can exploit to gain access to your network - even if you use strong encryption.
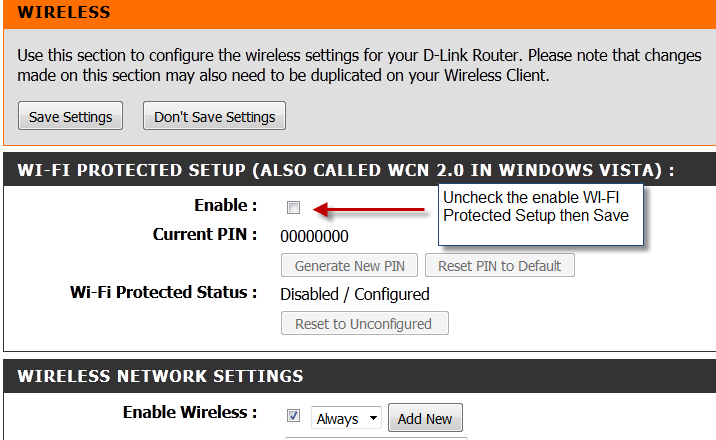
Source: Steve Shank
In addition to WPS, consider disabling:
- UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) - can open network ports without your knowledge
- Remote router management - unnecessary unless you truly need it
- Unused services or ports enabled by default
If you’re not actively using a feature, it’s safer to turn it off.
How to secure these settings
- Log in to your router’s admin panel.
- Navigate to Advanced Settings or Security.
- Disable WPS and any features you don’t recognize or use.
- Save changes and reboot the router if required.
Why this matters
Every enabled feature is a potential entry point. By reducing unnecessary functions, you limit the ways attackers can interact with your router.
A simpler configuration means fewer risks - and a more secure Wi-Fi network overall.
Tip #6: Set Up a Guest Wi-Fi Network
If you regularly share your Wi-Fi with guests, friends, or visitors, giving them access to your main network can be a security risk. Once connected, their devices may be able to see or interact with other devices on your network.
That’s where a guest Wi-Fi network comes in.
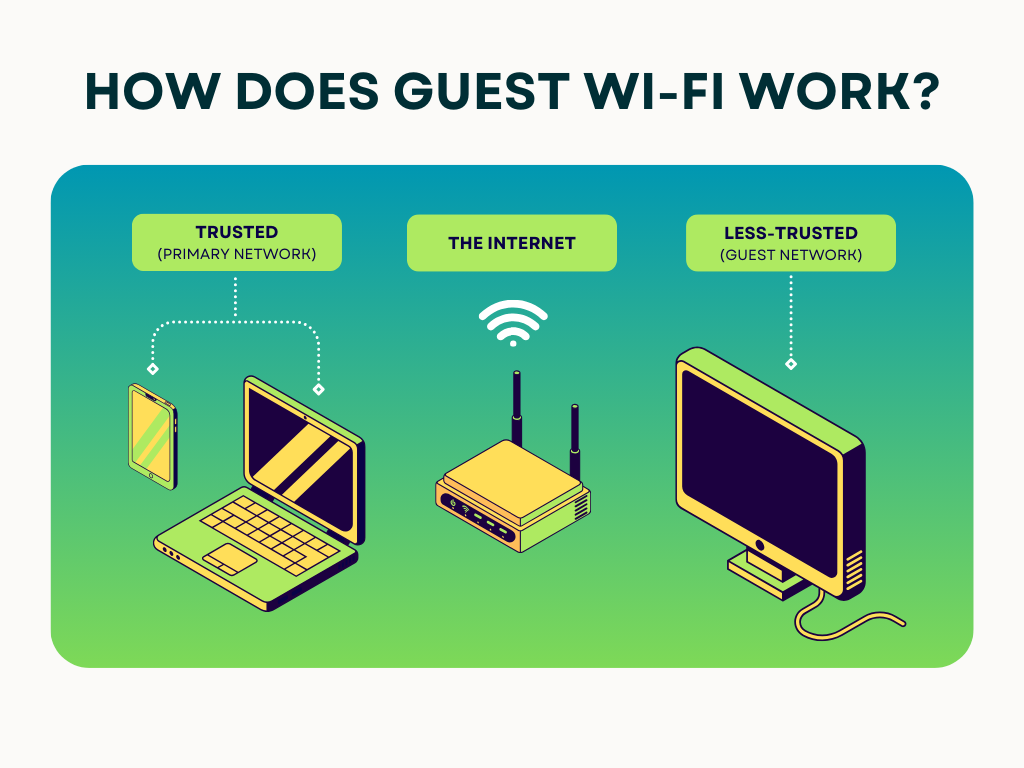
A guest network is a separate Wi-Fi connection created on your router. It:
- Uses a different password
- Keeps guest devices isolated from your main network
- Protects your personal devices and data
Most modern routers support this feature, and it’s easy to set up. Guest devices can introduce risks you don’t control, such as:
- Outdated software
- Malware or infected apps
- Weak device security
By isolating these devices, you reduce the chance that a problem on one device affects your entire network.
When a guest network is especially important
- Visitors connecting phones or laptops
- Smart home installers or service technicians
- Temporary access for rentals or shared spaces
You can also disable the guest network when it’s not needed.
Why this matters
A guest network keeps your primary Wi-Fi environment private and protected. Your computers, work devices, smart home systems, and personal data remain isolated - even when others are connected.
It’s a simple step that adds a strong layer of protection with almost no effort.
Tip #7: Monitor Connected Devices Regularly
Even with strong passwords and secure settings, it’s important to keep an eye on who is actually connected to your Wi-Fi network. Unauthorized devices can sometimes slip in unnoticed - especially if access was shared in the past.
Regular monitoring helps you catch problems early.
- Log in to your router’s admin panel.
- Look for sections like Connected Devices, Device List, or DHCP Clients.
- Review all devices currently using your Wi-Fi.
Most routers show device names, IP addresses, and connection status.
What to look for?
- Devices you don’t recognize
- Old phones, laptops, or gadgets you no longer use
- Suspicious or generic device names
If something looks unfamiliar, it’s worth investigating.
What to do if you find an unknown device
- Change your Wi-Fi password immediately
- Remove or block the device in router settings
- Review recent router activity if logs are available
Unknown devices can slow down your connection, consume bandwidth, or pose a serious security risk. Monitoring your network ensures that only trusted devices have access.
This habit keeps your Wi-Fi under control - and your data protected.
Tip #8: Add an Extra Layer of Protection with a VPN
Even a well-secured Wi-Fi network can’t protect everything. Once your data leaves the router and travels across the internet, it can still be exposed to tracking, monitoring, or interception - especially by ISPs or third parties.
This is where a VPN (Virtual Private Network) makes a real difference.
When you use a VPN:
- Your internet traffic is encrypted before it leaves your device
- Your real IP address is hidden
- Your online activity is protected from ISPs, network monitoring, and eavesdropping
This applies not only to public Wi-Fi, but also to home networks.
Why a VPN matters even on secured Wi-Fi
A VPN helps protect you from:
- ISP tracking and traffic logging
- Data interception on compromised or misconfigured routers
- IP-based attacks and profiling
- Privacy risks when working remotely or accessing sensitive accounts
In short, it secures what your router alone cannot.
VPN Guru adds a powerful privacy layer on top of your Wi-Fi security:
- Strong encryption for all internet traffic
- No-logs policy for true online privacy
- Easy-to-use apps for all major devices
- Protection on both home and public Wi-Fi
With VPN Guru enabled, your data stays private - no matter where or how you connect.
Why this matters
Wi-Fi security starts at the router, but it doesn’t end there. A VPN ensures that your online activity remains private even beyond your home network.
It’s the final step that turns a secure Wi-Fi setup into a truly protected online environment.
Lock Down Your Wi-Fi, Protect What Matters
Your Wi-Fi network is the foundation of your digital life. From personal messages and online banking to work files and smart home devices, everything depends on how well it’s protected.
As you’ve seen, securing your Wi-Fi doesn’t require complex tools or advanced technical skills. Simple steps - like changing default credentials, using strong encryption, keeping your router updated, and monitoring connected devices - can dramatically reduce your exposure to common threats.
But true security goes beyond your router.
By adding a VPN, you ensure that your internet traffic stays encrypted and private even after it leaves your home network. With VPN Guru, your data is protected on every connection - at home, at work, or on the go.
Take control of your Wi-Fi security today and keep your online activity where it belongs: private.