What is VPN? Born for Corporations, Adopted by Millions

Although they may seem like a relatively new privacy tool, virtual private networks, or VPNs, have been around since the late 1990s. The first VPN protocols were developed by Microsoft engineers with the goal of enabling remote workers to safely access company networks via the open internet. The objective was straightforward at the time: create an encrypted "tunnel" to prevent competitors or attackers from intercepting data.
More than two decades later, this purpose hasn’t disappeared-but the role of VPNs has expanded far beyond its original corporate use case.
Today, VPNs serve millions of everyday users who rely on them not only for secure remote access but also for privacy, protection on public Wi-Fi, bypassing geo-blocks, and avoiding tracking by advertisers and ISPs. What started as a niche enterprise technology has become one of the most widely used online security tools of the modern internet.
What Is a VPN? (In Simple Words)
In essence, a virtual private network, or VPN, is a tool that creates an additional layer of security between you and the internet. A VPN routes all of your traffic via a private, secure server rather than allowing your device to connect to websites directly. It replaces your actual IP address with a new one and encrypts your data along the way.
The simplest way to think about it is that a VPN forms a sort of private tunnel for your internet activity. Within this tunnel:
- The outside world cannot see what you're doing.
- Websites don't always recognize the source of your connection.
- And it becomes very difficult for anyone to read or intercept any data you send or receive.
Originally, VPNs were mostly a corporate thing-companies used them to let remote employees safely connect to internal networks. But that’s changed completely. Today, millions of everyday users rely on VPNs for simple, practical reasons: staying safer on public Wi-Fi, getting around regional restrictions on streaming platforms, or just keeping advertisers and internet providers from tracking every click.
In short, a VPN gives you more privacy, more control, and a much safer experience whenever you go online.
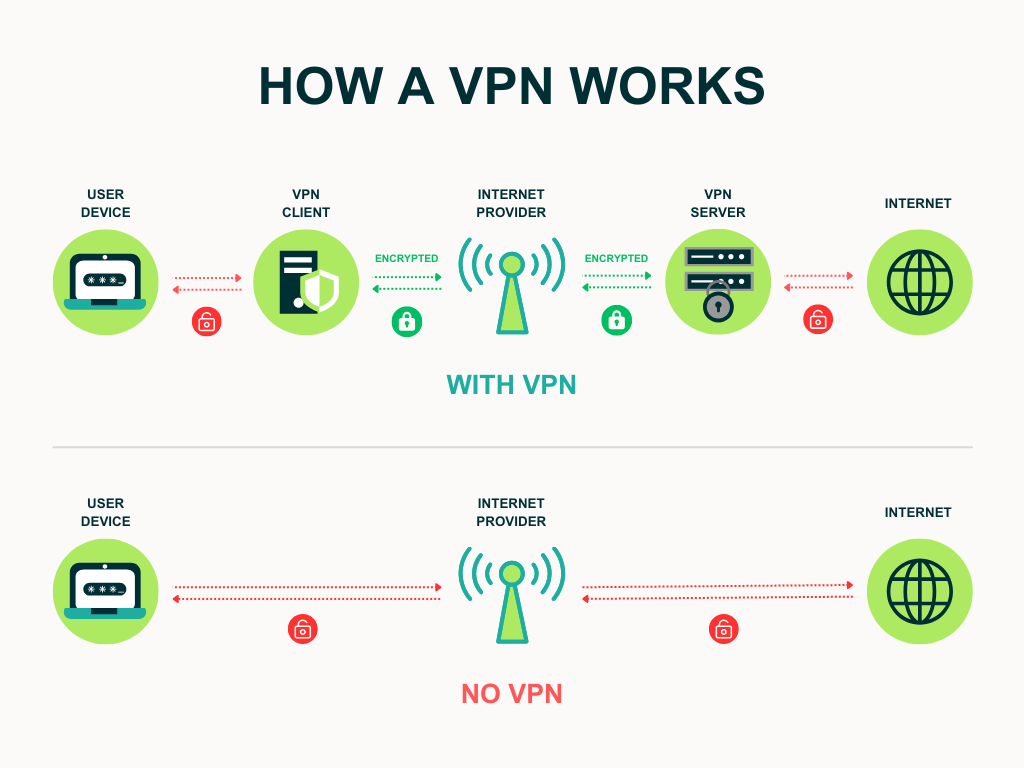
How a VPN Works Behind the Scenes
When you turn on a VPN, your device connects to the internet in a few important ways. Instead of talking directly to websites or apps, your data travels through a dedicated, encrypted pathway that keeps it safe from interception or tracking. Here’s what happens:
Step 1. Encryption Protects Your Data
The moment you activate a VPN, it encrypts all traffic leaving your device. This means your browsing activity, search queries, messages, and any other data sent out are turned into unreadable code. Even if someone intercepts the connection, like a hacker on public Wi-Fi or an overly curious ISP, they only see scrambled data with no meaningful content.
Step 2. A Secure Tunnel Is Created
Next, the VPN sets up a secure communication tunnel between your device and a VPN server. This tunnel keeps your traffic separate from the open internet. It stops third parties from monitoring your activity or injecting anything into your connection. Think of it as sending your data through a private, locked corridor instead of a public highway.
Step 3. Your IP Address Is Hidden and Replaced
Once your data reaches the VPN server, your real IP address is replaced with the IP of the server you are connected to. This makes it appear as if your online activity is coming from the server’s location instead of your own. As a result, websites and apps see only the VPN server’s IP, which helps protect your identity, location, and device details.
Step 4. The VPN Server Forwards Your Traffic to the Internet
From the server, your traffic is decrypted and sent to its final destination, whether that’s a website, a game server, or an app. The return data follows the same path back (first to the VPN server, then through the encrypted tunnel to your device) ensuring ongoing protection.
Step 5. Modern VPN Protocols Keep the Process Fast and Secure
Behind the scenes, VPNs use secure connection protocols, which are rules that define how data is encrypted and sent. The most common protocols today include:
- WireGuard - fast, modern, lightweight.
- OpenVPN - highly secure and widely trusted.
- IKEv2/IPsec - stable and efficient, especially for mobile use.
Different VPN providers may offer several protocols so users can balance speed, security, and compatibility.
What a VPN Does NOT Do (Common Myths)
VPNs are incredibly useful, but they’re not magic. A lot of people expect them to solve every online privacy or security problem, and that’s where disappointment, and confusion usually comes in. Here are a few things a VPN doesn’t do, no matter which provider you choose.

- A VPN doesn’t make you completely anonymous
A VPN hides your IP address and encrypts your traffic, yes, but that doesn’t mean you become invisible online. Websites can still identify you through cookies, accounts you’re logged into, your browser settings, and dozens of other signals. If you sign into Google or Instagram, they still know it’s you.
- It won’t protect you from viruses or scams
A VPN isn’t an antivirus and can’t block malware, fake websites, phishing messages, or anything you accidentally download. It protects your connection, not the files or links you interact with.
- It won’t magically speed up your internet
Some people expect a VPN to “boost their connection.” In reality, it usually does the opposite: encryption and rerouting add a bit of overhead. A good VPN keeps this slowdown minimal, but it’s still not a performance booster.
- It doesn’t hide your activity from websites you’re logged into
If you’re signed in to a service - Netflix, Amazon, YouTube, Gmail - that platform still knows what you do there. A VPN doesn’t block your account-level history.
- A VPN can’t protect you from yourself
If you overshare personal info on social networks, use the same password everywhere, or click suspicious links, no VPN will save you. Online safety is a mix of tools and habits.
Different Types of VPN Protocols
Not all VPNs are created equal - a big part of the difference comes from the underlying protocol they use. Protocols define how data is encrypted, transmitted, and secured, and choosing the right one can impact both speed and privacy. Here’s a breakdown of the main VPN protocols used today.
IPSec VPN
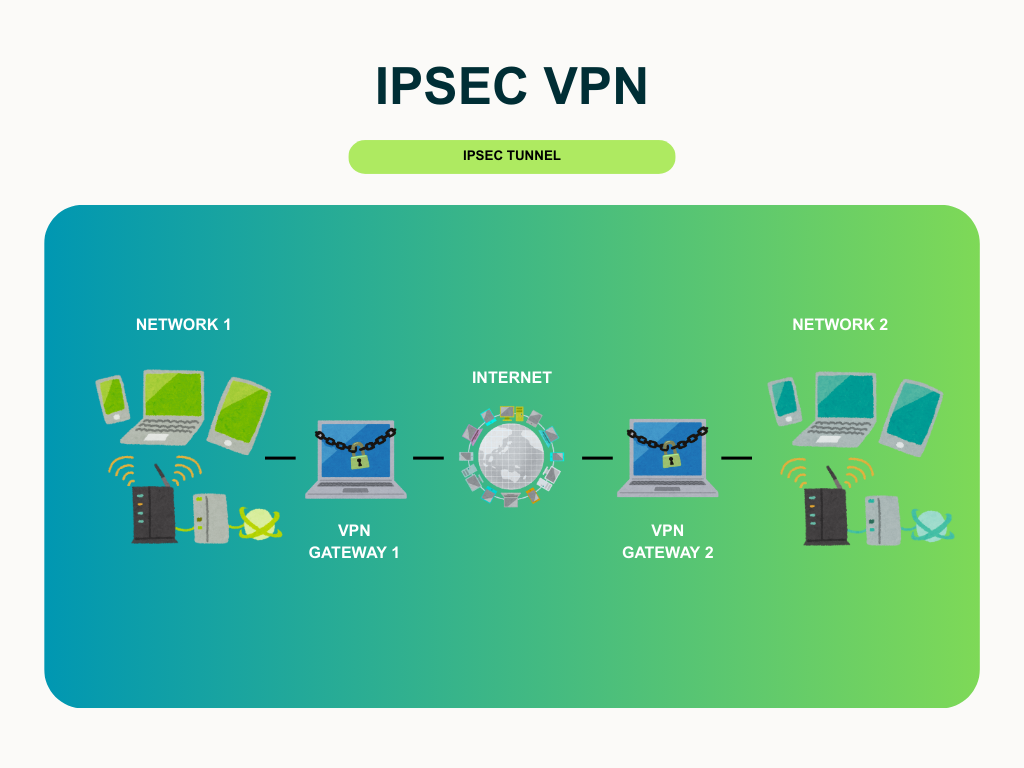
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) is one of the most widely used VPN protocols, designed to secure data at the network layer of the OSI model. It creates an encrypted tunnel between devices and servers, ensuring data remains confidential, untampered, and authenticated.
IPSec VPN:
- Encrypts all transmitted data
- Verifies that data hasn’t been altered using hashing
- Confirms the identity of connected devices via pre-shared keys or certificates
- Prevents duplication of packets
IPSec VPNs are commonly used by enterprises for remote access and site-to-site connections. While highly secure, setup and configuration can be complex, requiring technical expertise.
L2TP VPN
The Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) combines elements of PPTP and L2F, providing reliable tunneling capabilities. Alone, L2TP offers tunneling and encryption but not full confidentiality. It is often paired with IPSec to secure sensitive data transmissions, securing business communications and sensitive data exchanges.
Additional encryption can reduce speed, so it may not be ideal for users who prioritize performance.
PPTP VPN
The Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is known for simplicity and wide platform support. Operating at the data-link layer, it’s easy to set up and fast, making it suitable for streaming or gaming.
PPTP uses TCP port 1723 and wraps PPP packets using GRE. While convenient, its security is considered weak compared to modern protocols, so it’s generally not recommended when privacy is critical.
SSL VPN
SSL (Secure Socket Layer) VPNs are web-based, allowing secure access to applications, portals, or internal resources directly through a browser. No additional software installation is needed, making it user-friendly and accessible from virtually any device.
SSL VPN:
- Encrypts traffic via SSL/TLS, protecting privacy and data integrity.
- Ideal for remote access without exposing the full network.
However, not that ideal for resource-intensive applications requiring full network access.
TLS VPN
TLS (Transport Layer Security) VPNs leverage the same cryptographic principles as HTTPS to create a secure connection between users and networks.
The protocol has two layers:
- TLS Record Protocol ensures secrecy and reliability
- TLS Handshake Protocol secures shared data and verifies identity
TLS VPNs combine strong encryption with comparatively high speeds, making them suitable for VoIP, file sharing, and remote work.
OpenVPN
OpenVPN is an open-source protocol that uses the OpenSSL library, offering flexible encryption options and strong security. Its cross-platform support and ability to bypass firewalls make it highly versatile.
Why it’s popular:
- Continuous community-driven development
- High compatibility with multiple platforms
- Reliable security and performance balance
SSH VPN
Built on the SSH protocol, SSH VPNs create a secure, encrypted channel for remote access and command-line operations. They are commonly used by system administrators and technical users for quick, effective network protection.
VPN vs. Other Privacy Tools
VPNs are just one of several tools people use to protect their online privacy. While they all aim to improve security or anonymity, each has its own strengths and limitations. Here’s a quick comparison with some commonly used alternatives.
VPN vs. Proxy

VPN vs. Tor

VPN vs. Smart DNS
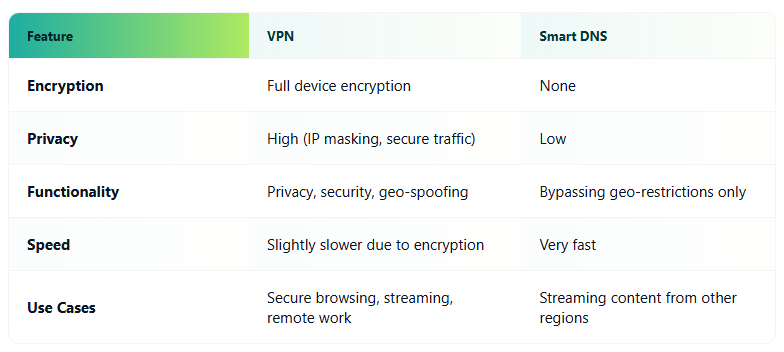
VPNs provide the most balanced combination of privacy, security, and flexibility. Proxies are lightweight but limited, Tor offers the highest level of anonymity at the cost of speed, and Smart DNS focuses solely on location spoofing.
How to Choose a Reliable VPN Provider
Picking a VPN can feel overwhelming-every provider promises speed, security, and encryption. But the reality is that not all VPNs are equal. A good provider is defined by a few core principles that directly affect your privacy, security, and day-to-day experience. Here’s what to look for.
No-logs policy
A trustworthy VPN should never store records of your activity. This means no logs of your browsing history, connections, or the servers you use. No logs = no data to hand over, leak, or misuse. This is the foundation of privacy and the main reason people install a VPN in the first place.
Speed and stability
VPN encryption adds some overhead, but a quality provider minimizes this so you barely notice the difference. Fast and stable connections let you stream, game, and work without interruptions-a key benefit of a good VPN in daily life.
Server network size and geography
The more servers and locations a VPN has, the better your experience will be. For example, you can avoid overcrowded servers and access content from other regions, picking a nearby server for better performance. A large, well-distributed network improves both speed and reliability while giving more options for location-based access.
Supported protocols
The underlying VPN protocols define how your data is encrypted and transmitted. Modern protocols like WireGuard, OpenVPN, and IKEv2/IPsec balance speed and security. Make sure your provider offers a range of protocols so you can choose the best combination for your needs.
Kill Switch & Split Tunneling
Some adnvanced features may go beyond basic encryption:
- Kill Switch automatically blocks internet access if the VPN drops, preventing accidental exposure of your IP.
- Split Tunneling lets you choose which apps use the VPN while others connect directly, saving bandwidth and maintaining flexibility.
These features make the VPN more robust and practical for everyday use.
Company transparency and audits
Trustworthy providers are open about their operations.
- Look for companies that publish independent security audits
- Make their privacy practices clear
- Update users about changes or incidents
Protect Your Privacy the Smart Way
A good VPN delivers real privacy, fast speeds, up-to-date tech, and features you’ll actually use. The right provider keeps your info locked down and your life online running smooth, no matter what you’re doing.
If you want all that in one package, check out Guru VPN. They’ve got servers in 49+ countries, connections built for gamers, and straightforward apps that work on pretty much any device. Streaming, gaming, working from home-it all feels easy and secure.
Online safety shouldn’t be a hassle. With a decent VPN, you’re protected in seconds.